Galanin: A Promising New Treatment for Migraine with Aura
Cerebral TorqueShare
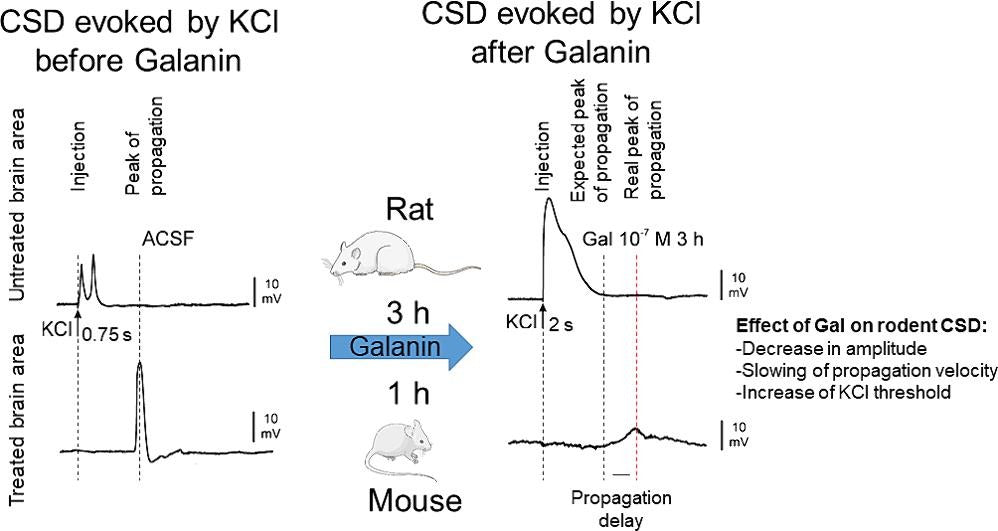
A recent study has found that galanin, a neuropeptide, may be a potential new treatment target for migraine with aura. Galanin significantly reduced the severity and spread of cortical spreading depolarizations (CSDs), which are believed to be the underlying cause of visual, sensory, and language disturbances during migraine aura.
The study, conducted on rats and mice, revealed that galanin:
1.Reduced CSD amplitude and propagation speed in the brain
and
2. Increased the threshold of stimulation required to trigger CSDs
These findings suggest that developing galanin agonists can enhance galanin's effects in the brain and could offer a novel approach to managing migraine with aura.
Stopping or reducing the severity of CSD could benefit migraine patients in several ways:
1. Reduced aura symptoms: By inhibiting CSD, visual, sensory, or language aura may be lessened or eliminated.

2. Decreased migraine pain: CSD may trigger or worsen migraine headache pain. Stopping CSD could potentially reduce the intensity or duration of migraine headaches.
3. Improved quality of life: Minimizing aura symptoms through CSD inhibition may allow migraine patients to experience less disability.
4. Potential prevention of migraine chronification: Frequent migraine attacks with aura have been linked to an increased risk of developing chronic migraine. Targeting CSD may slow or prevent the progression from episodic to chronic migraine.
5. Reduced risk of associated neurological conditions: Migraine with aura may be associated with an increased risk of certain neurological conditions, such as stroke. Stopping CSD could potentially reduce this risk.
While further research is still necessary to validate these results in humans, the identification of galanin as a potential treatment target is significant.


